An opportunity to reduce global burden of stroke-related disability
Contact: Steven Lee, (210) 450-3823, lees22@uthscsa.edu
SAN ANTONIO, Feb. 4, 2026 – For many stroke survivors, recovery is derailed by painful muscle stiffness and involuntary spasms that limit movement, independence and quality of life. Often viewed as an unavoidable consequence of stroke, this condition – known as post-stroke spasticity – may instead represent a missed opportunity for earlier, more effective care.
Two researchers at UT Health San Antonio led the writing group for a new scientific statement focused on post-stroke spasticity for the American Heart Association. The statement urges a shift in how post-stroke spasticity is recognized and treated, emphasizing early diagnosis, timely intervention and innovative therapies to reduce long-term disability and improve recovery after stroke.

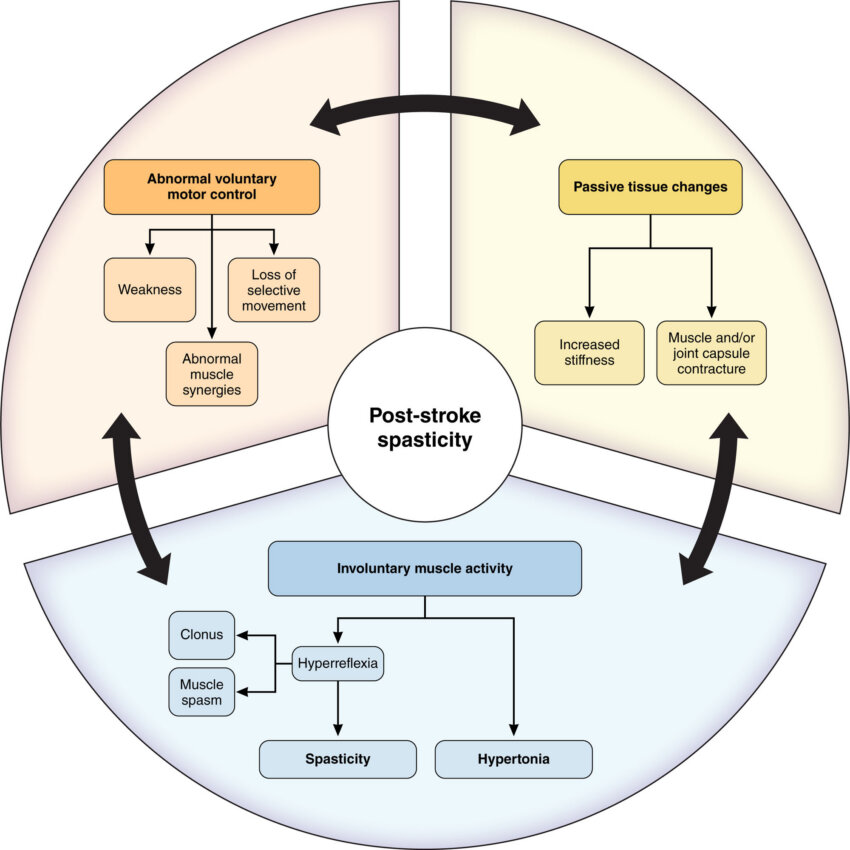
Post-stroke spasticity causes abnormal muscle tightness and involuntary spasms that can interfere with walking, arm use, daily activities and participation in rehabilitation. It affects an estimated 30% to 80% of stroke survivors, contributing to higher healthcare costs, increased caregiver burden and preventable complications, such as pain, joint contractures and loss of mobility.
“I see patients every week whose recovery is limited not by the stroke itself, but by muscle stiffness and spasms that were never addressed early,” said Sujani Bandela, MD, a neurologist at UT Health San Antonio, the academic health center of The University of Texas at San Antonio. She also is vice chair of the Neural Repair and Rehabilitation Section at the American Academy of Neurology, first author of the heart association’s scientific statement and vice chair of its writing group. “When spasticity is recognized and treated sooner, we often have a real opportunity to preserve movement, reduce pain and help patients stay engaged in their rehabilitation.”
The heart association’s scientific statement highlights growing evidence that earlier recognition – often within the first three months after a stroke – combined with coordinated rehabilitation and medical therapies may improve functional outcomes and reduce long-term disability. Yet many patients experience delayed diagnosis or receive little or no rehabilitation support, particularly in rural areas and communities with fewer resources.

“Advances in neuroscience, rehabilitation and technology are giving us new tools to intervene earlier and more effectively after stroke,” said senior author of the statement and chair of its writing group, Mark P. Goldberg, MD, professor of neurology and Edward B. LeWinn M.D. Memorial Chair at UT Health San Antonio, and chair-elect of the heart association’s Rehabilitation and Recovery Committee within the Stroke Council. “This scientific statement reflects the growing evidence that earlier, targeted approaches to spasticity could meaningfully improve long-term outcomes for stroke survivors.”
The scientific statement advises:
- Greater awareness among patients, caregivers and health care professionals
- Proactive monitoring of patients at high risk for developing spasticity
- Coordinated, multidisciplinary care including rehabilitation and medical therapy
- Innovative care models, including telehealth, to improve access to specialized care
Access to specialized stroke rehabilitation remains limited in many parts of South Texas and other regions with fewer resources, contributing to persistent gaps in post-stroke recovery. Researchers note that expanding early spasticity care could help reduce long-term disability and improve quality of life for stroke survivors across the region.
“Stroke survivorship is increasing, but recovery is not equal for everyone,” Goldberg said. “Improving early access to spasticity care is an important step toward better short- and long-term stroke recovery for all patients.”
The statement, titled, “Early Recognition and Intervention for Poststroke Spasticity: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association,” published Jan. 29, 2026, in Stroke, the American Stroke Association’s flagship, peer-reviewed journal (the American Stroke Association is a division of the American Heart Association).
Goldberg is scheduled to present the statement at the association’s International Stroke Conference 2026 in New Orleans on Friday, Feb. 6. Bandela is scheduled to present a course session with a group on spasticity and different case presentations. See conference details, here: ISC26 Planner.
Early Recognition and Intervention for Poststroke Spasticity: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association
Sujani Bandela, Laura McPherson, Richard L. Harvey, Oluwole Awosika, Dipika Aggarwal, Charles Y. Liu, Preeti Raghavan and Mark P. Goldberg, on behalf of the American Heart Association’s Stroke Council, the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, the Council on Basic Cardiovascular Sciences, and the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health
The full scientific statement is available at:
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STR.0000000000000515
Published Jan. 29, 2026: Stroke (AHA/ASA Journals)
Link: Top Things to Know: Early Recognition & Intervention for Poststroke Spasticity
UT Health San Antonio is the academic health center of The University of Texas at San Antonio (UT San Antonio), offering a comprehensive network of inpatient and outpatient care facilities staffed by medical, dental, nursing and allied health professionals who conduct more than 2.5 million patient visits each year. It is the region’s only academic health center and one of the nation’s leading health sciences institutions, supported by the schools of medicine, nursing, dentistry, health professions, graduate biomedical sciences and public health that are leading change and advancing fields throughout South Texas and the world. To learn about the many ways “We make lives better®,” visit UTHealthSA.org.
Stay connected with UT Health San Antonio on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram and YouTube.